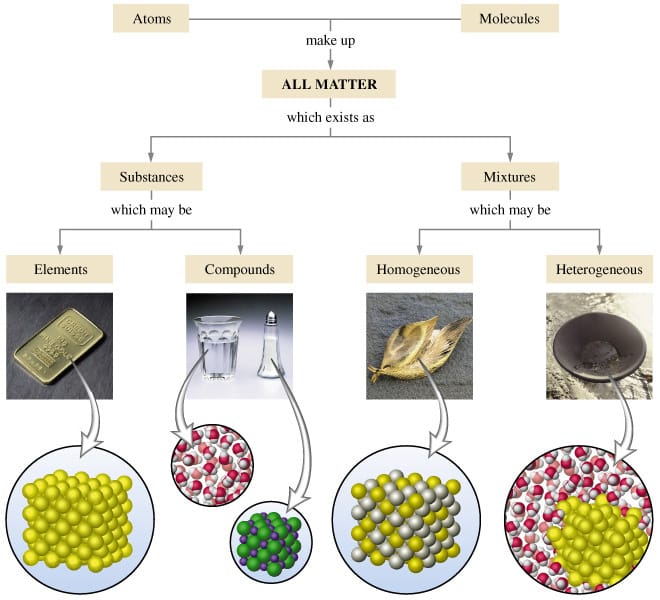
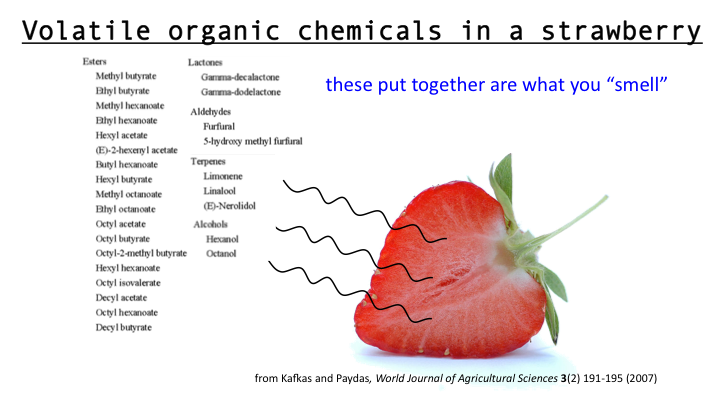
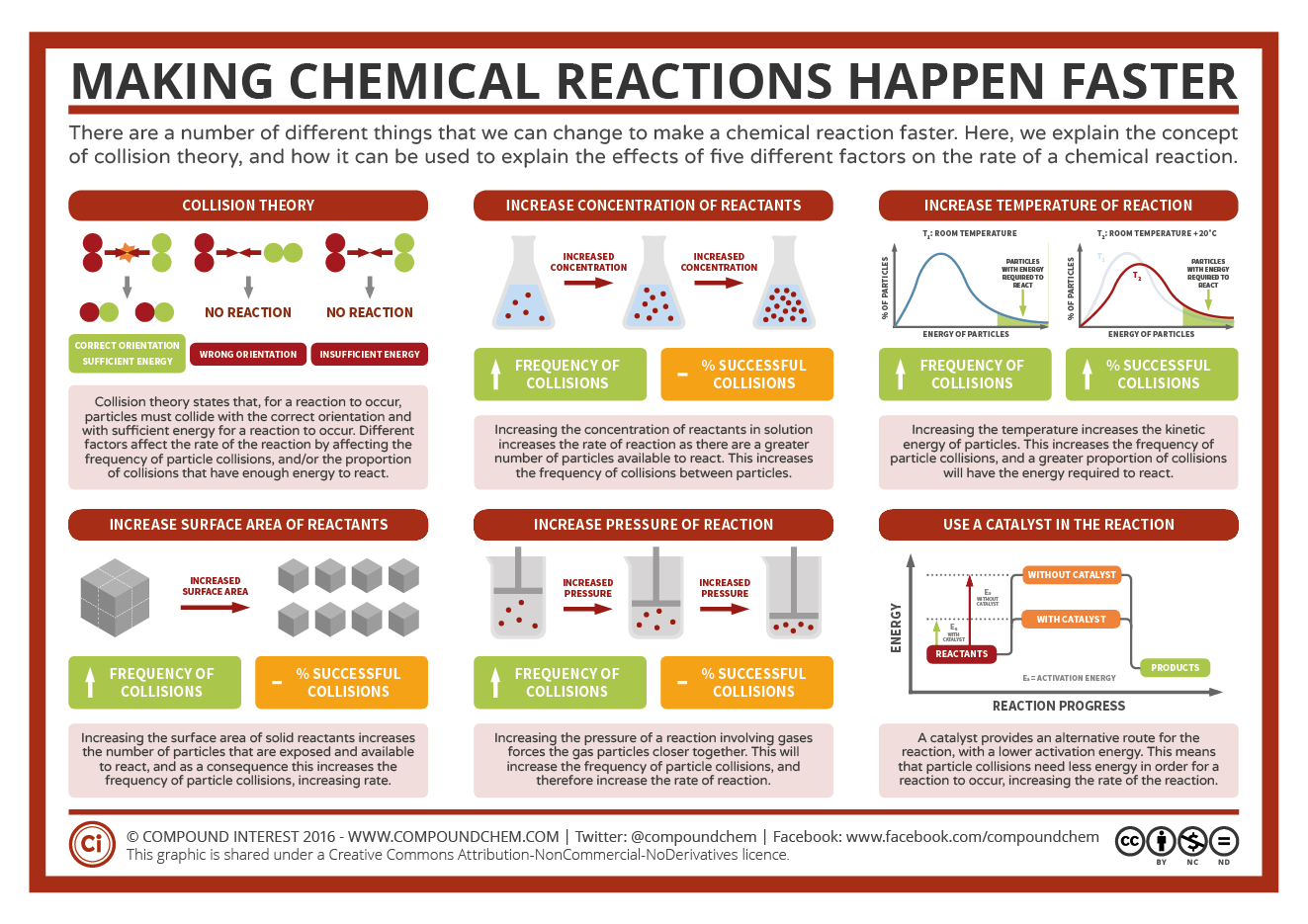
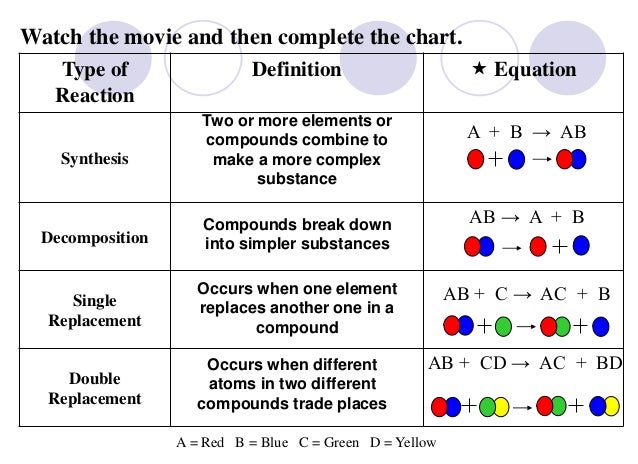
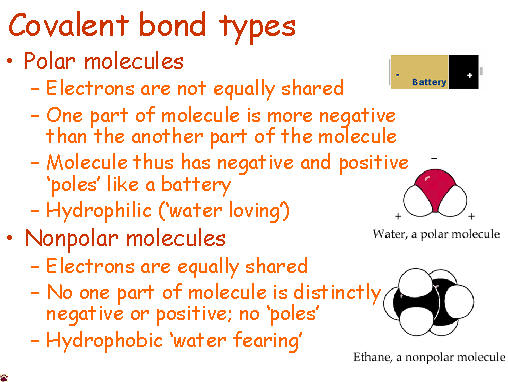
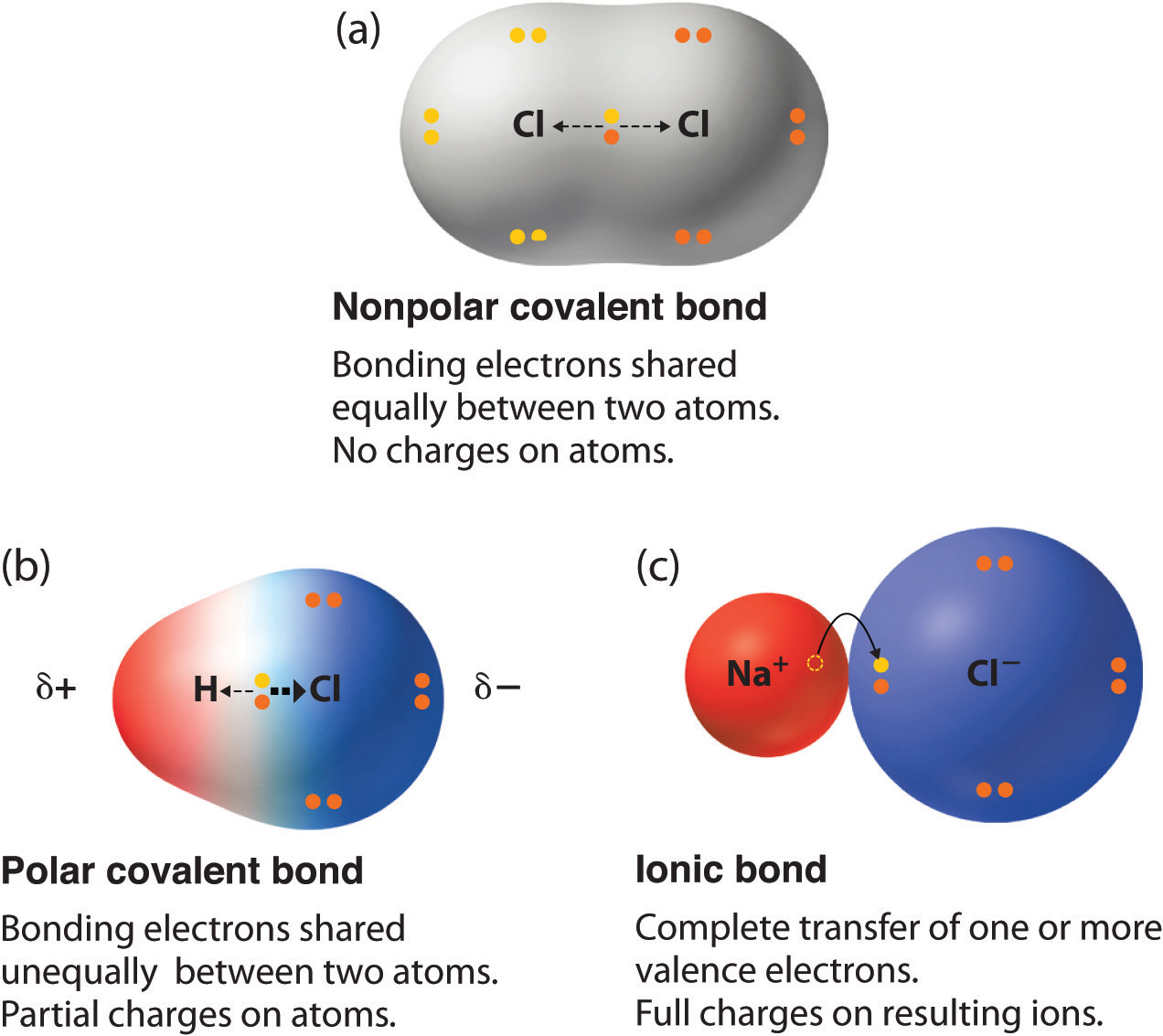
Today we discussed matter. Everything in the universe is made up of matter. Matter can be classified as substances of mixtures. A substance is pure and is either made up of elements, the simplest form of matter found on the periodic table, or compounds - two or more atoms chemically combined that can be represented with a formula (ie. H2O).
A mixture is two or more things (substances or anything really) in the same place at the same time. Salt water is a tricky one because we know we can write a formula for salt (NaCl) and water (H2O), but it is a mixture because when mixed in solution, these compounds do not combine.
Mixtures can be heterogeneous of homogeneous based on how the solute is spread through the mixture. Heterogeneous mixtures are not mixed evenly and each sample could be different - like salad, chocolate chip cookie dough ice cream, air, and soil. Homogeneous mixtures are the same throughout like creamy peanutbutter, vanilla ice cream, pure air, sugar, and kool-aid.


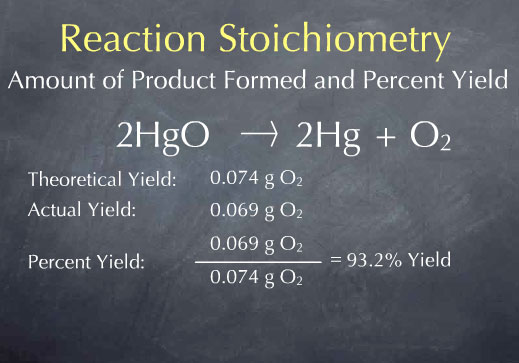
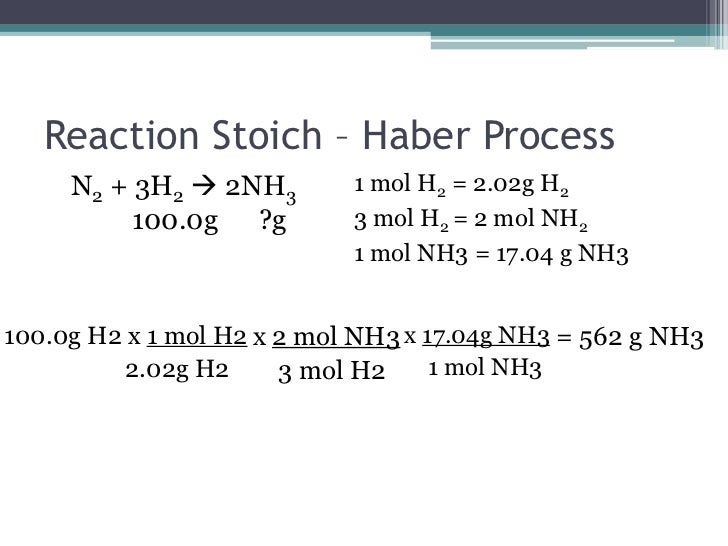
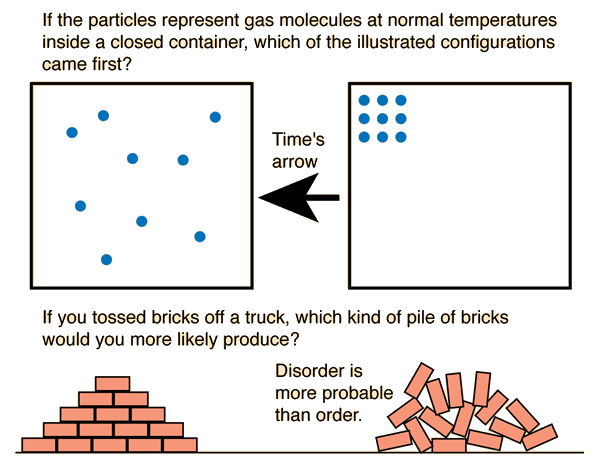
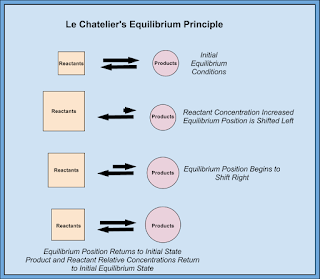
One important thing we discussed today was the Law of Conservation of Matter proposed by Lavoisier. Basically matter cannot be created or destroyed... it is conserved or recycled or moved somewhere else, but it cannot magically appear or disappear!