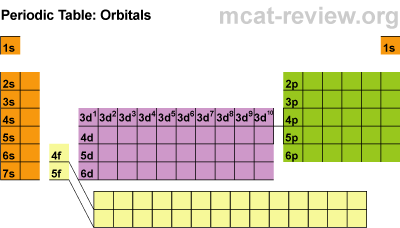
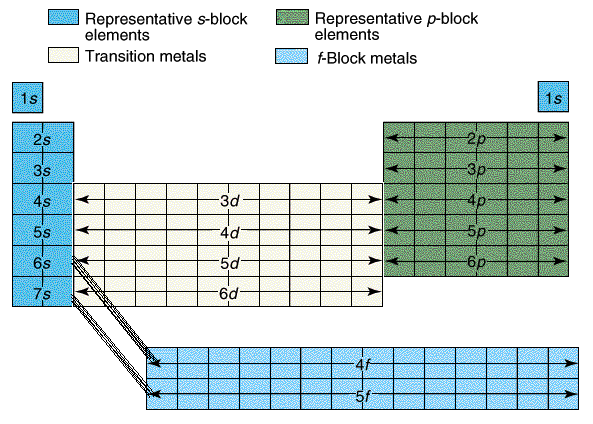
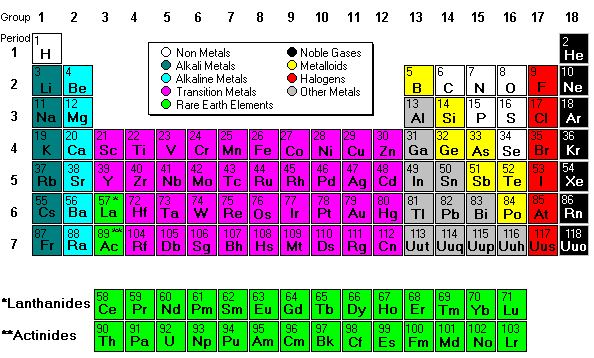
It is all about the electrons! Always!
Electro- negativity is how badly atoms want electrons. The most electronegative atoms are Fluorine, Chlorine, and Oxygen. Everyone wants to be a Noble Gas... and halogens are the closest so they are the most electronegative.
Ionization energy is how difficult it is to remove electrons. It is difficult to remove electrons from atoms that are electronegative.
Atomic radius increases as you move down the periodic table because atoms have more mass, but actually decreases from left to right because atoms are holding on to their electrons tighter (because they are more electronegative).
Shielding has to do with how protons are blocked by the electron shells - the more shells there are, the more blocking there is. So something in period 5 (with 5 shells) has more shielding than an element in period 2 with two electron shells. Sheilding is constant across the periodic table because the number of shells is constant.